Abstract
Today we are definitively getting to a point where it becomes challenging to draw the line between a household product being bought and built to serve its consumer, and that same product being designed and equipped for serving other entities beyond the knowledge of its official owner.
Many forms of technological progress converged to get us to a point where it becomes ambiguous and unclear what is the full scope of the sophisticated technological products that are all around us and so often extremely affordable, in spite of its immense capabilities. One of the most obvious examples is of course the smartphone. Its computing power often overlaps that of a personal computer, while still fitting in a pocket and having a plethora of sensors and hardware features, some of which the user may never know these are present and for what purpose these serve.
At home, is more and more the normal scenario to have the most prosaic devices, such as light bulbs and switches, all equipped with a chip that renders these connected to the Internet. Once this is done, all bets are off. For the consumer is very convenient, because at the reach of an app, one can control and monitor his property or perform tasks remotely.
Today is a bit of a gamble. Between the comfort and convenience provided by technology in the realm of the home environment, there is also the security risk, privacy and the user being manipulated and targeted by manufacturer campaigns, or its information sold to third parties for similar purposes.
Still, however powerful and discrete these technologies might be, the greatest joy lies in leveraging its power for the own use, and that is, with no strings attached, and the user really running the show.
That is where I like to sit at. It is true that for IoT tech to become so abundant, cheap, and with routes for open use, the fact is that intentionally or not, manufacturers (regardless of their agendas) gave way for the communities to build on their hardware, but ultimately not being dependent of their clouds and platforms. Projects like Tasmota or ESPHome are one such example, where off-the-shelf products like bulbs and switches are often modified/reflashed to run one of these firmwares.
Concept
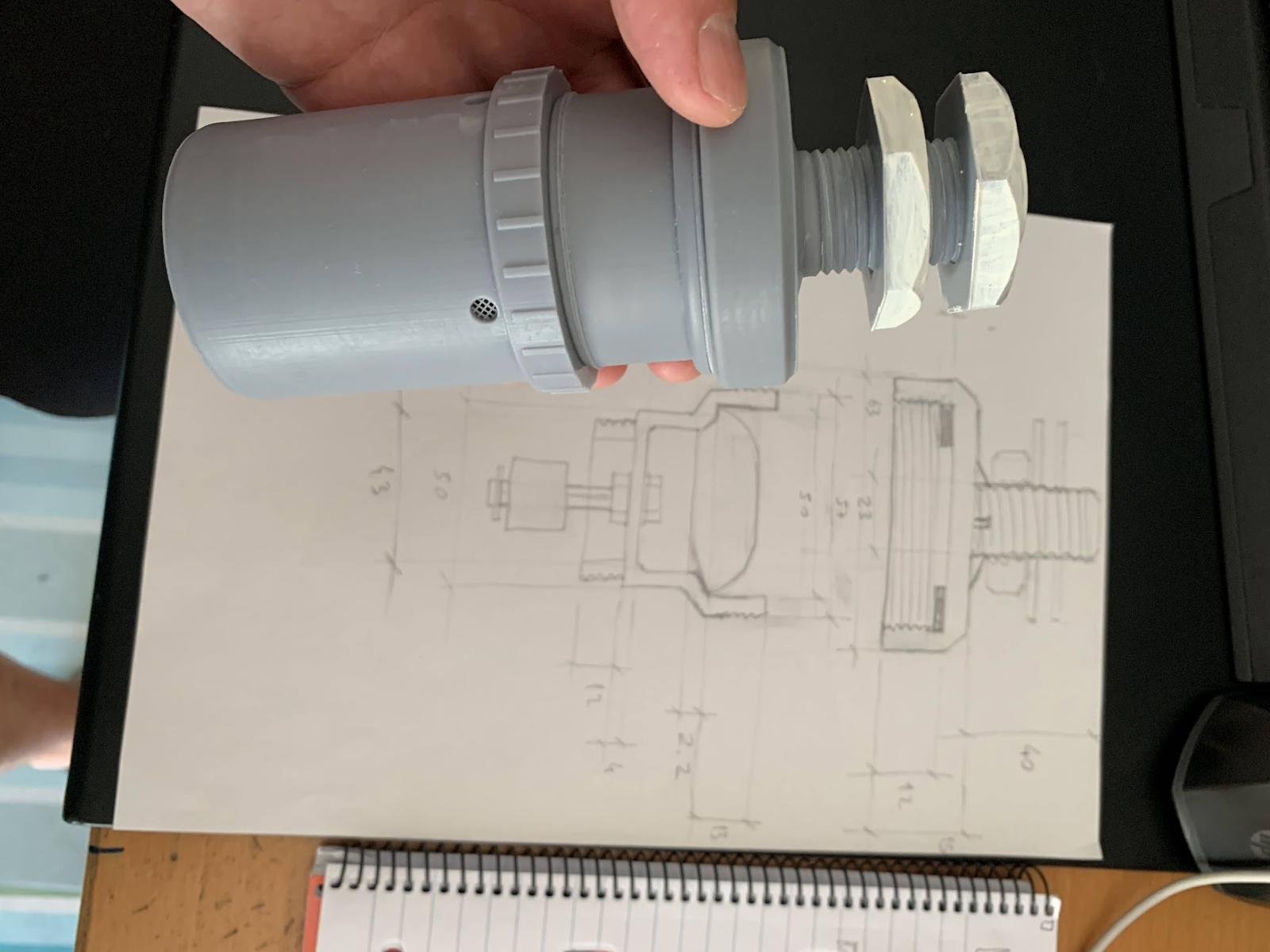
Here I am presenting a bit of a different approach though. Starting with a very conventional insect zapper with nothing that can be pinged from the Internet (no electronics whatsoever - a couple of light bulbs, a ballast, two starter switches, and a Cockcroft–Walton multiplier for generating the HV to zap the insects), I wanted to integrate it better in home automation without requiring external devices such as Wifi sockets or such.
Implementation
And so I went. The first iteration was to put an ESP32 relay board on it. I used the "ESP32_Relay X1" board which I had used in previous projects with good results. This board has the advantage of having an integrated 230 V insulated SMPS, making it very convenient for integrating in mains powered devices:
But then for me it felt boring to just be able to turn the zapper on and off. What about if I could also detect and count the number of times the zapper would kill insects? That could be fun.
And so I decided to go to the 2nd stage. The ESP32, as some of you might know, has plenty of GPIO ports, and is overall a much more eclectic chip than its predecessor, the ESP8266. One can connect digital signal inputs, as well as DC analog signals to some of these pins, and use the data and events for their projects.
My challenge was to be able to sense the insect getting zapped. My first assumption was that when an insect gets zapped, there is a burst of current flowing across the HV power supply of the zapper. But measuring this HV current could be tricky do to safely and without a lot of precautions. Also I did not want to spend too much time with this project and to risk hardware and especially my health with iterations. So I went for an option that seemed a bit safer and that could also provide results. The idea was to measure the mains AC current on the input side of the HV power supply.
Unsurprisingly in most products of this kind, this device uses a Cockcroft–Walton multiplier for generating the HV. There is basically a set of diodes and capacitors (9 capacitors and 9 diodes to be more exact) where each pair of diodes and capacitors forms a stage. In this case we have 4.5 stages, which means that the output voltage can reach close to 2 * 4.5 times the input voltage Vpp. In this case it means approximately 2070 Volts.
This curcuit also has three resistors. One or two I presume are for limiting the input current (without it there would be one massive jolt of current for recharging the capacitors), while the other acts as a bleed resistor, to make sure the capacitors are discharged before someone might think of putting the fingers where is not supposed to.
So my idea was to (non-invasively) tap into the phase or neutral lines of this AC input in order to measure the current. My expectation was that during and after a zap there should be a flow of current, therefore making it possible to detect the insect getting zapped. For that effect I grabbed one of these CT boards sold cheaply on Aliexpress:
I did a modification on it however: first these have a capacitor that removes the DC offset from the LM358 opamp output. I didn't want that, because I had to supply a positive signal to the ESP32 ADC input. Secondly, these boards output a voltage that varies with the current signal. In this case the AC signal could be difficult to deal with. So I removed the capacitor, replaced it with a diode, and added a 4.7 uF capacitor in parallel with the output. This way I had a stable signal with no ripple, and more or less proportional to the current. Easier to measure by the ADC.
Connected it to GPIO34, which is the pin behind ADC1 of the ESP32, one of the pins that can be used by Tasmota:
In order to fix it, I added a ferrite bead to the 3.3 Volt rail, and twisted the wires going to the CT board around each other. And, yes instability was gone.
Once the hardware work was completed, it was time to play with the software! My first idea was to use Tasmota rules to detect when the ADC input would measure a value above a certain threshold. I tried this approach but it proved unsuccessful, as the short current pulses would rarely get detected. It is not clear from any of the project documentation, but apparently rules have evaluation periods that are too long for this scenario.
Without that option, the next best thing I could think of, was to define a driver in Berry (yes, with ESP32, Tasmota opens a whole new dimension of flexibility, by providing a scripting language in the firmware itself, that among many other things, allows the user to code drivers for devices not supported natively by Tasmota), and use its every_50ms callback to put the pulse detection cycle inside.
As such, in a driver we can define code that will get called every 50 ms (that is the maximum you can go). Taking advantage of that, I wrote a small driver that would read the ADC1 pin, and check if the value would be above a certain threshold or not. The threshold I have empirically verified as being a probable discharge and less likely to be noise related. Everytime the threshold is crossed, the driver will publish a message to a specific MQTT topic.
To have a consumer for that event, I configured Home Assistant to subscribe and handle it as a MQTT event:
Testing
For testing (because you don't have flies around when you need them), I picked up a plastic stick, attached a strip of paper to it, and wet the tip. Then by approaching that paper tip from the electrode bars I was able to provoke a discharge the same way an insect would.
And sure enough I was able to produce events: